Large Language Models (LLMs): The Future of Artificial Intelligence
1. What are LLMs?
Large Language Models (LLMs) are a type of artificial intelligence (AI) program designed to process and generate natual language text. Basically, LLMs are trained on large amounts of textual data from various sources, enabling them to naturally understand and reproduce language. The models have been applied in various fields recently (see Figure 1).
The models are based on deep neural network architectures, often using Transformer models, first introduced in the seminal paper “Attention is All You Need” by Vaswani in 2017. The Transformer architecture has become the foundation for modern language models, including GPT (Generative Pre-trained Transformer) and BERT (Bidirectional Encoder Representations from Transformers), to name but a few.

Figure 1. Applications of LMMs
2. How do LLMs work?
Large Language Models (LLMs) operate by learning to predict the next word in a sequence of text based on prior context. The process includes three primary phases: pre-training, fine-tuning, and reinforcement learning from human feedback (RLHF), as depicted in Figure 2. Firstly, LLMs are exposed to extensive texual datasets such as books, articles, and web contents, that have been gathered from the Internet during the pre-training phase. This phase allows the models to grasp the fundamental structure, semantics, and relationships within language. Next, the fine-tuning phase involves adapting pre-trained models, by further training on smaller, specific datasets to enhance the performance in particular tasks or specialized fields. Finally, RLHF is employed in some advanced models, such as GPT-4, to further enhance performance by incorporating feedback from human evaluators, ensuring the model better aligns with user expectations.
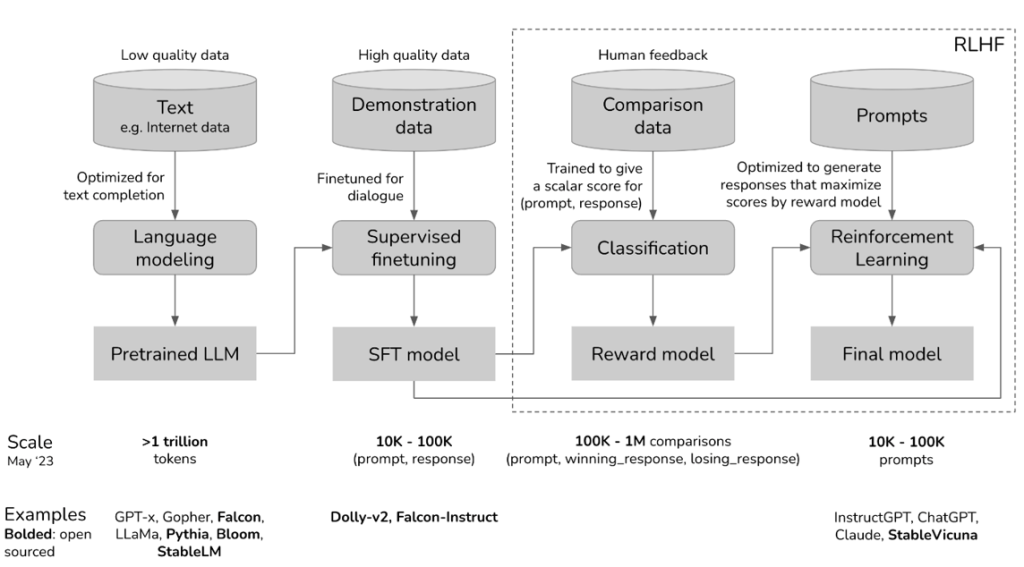
Figure 2. Diagram of three primary phases in LMMs
3. Applications of LLMs
The applications of LLMs are diverse and impactful across numerous domains. In natural language processing (NLP), LLMs are employed for tasks such as sentiment analysis, topic detection, and information extraction, revolutionizing how textual data is interpreted and utilized. Also, LLMs assist in drafting blogs, generating reports, composing poetry, or creating fictional narratives for content creation. Moreover, virtual assistants and question-answering systems like ChatGPT, Google Bard, and Alexa leverage LLMs to enable seamless, natural communication with users. Additionally, LLMs enhance automated translation systems, exemplified by the improved accuracy of tools like Google Translate. Finally, the models also support scientific research and data analysis by summarizing complex documents and handling large-scale data efficiently.
4. Advantages and Limitations of LLMs
The capabilities of LLMs are extensive, which excel in processing complex language structures, producing natural and coherent text, and adapting to various applications. These models improve productivity by automating repetitive tasks, thereby reducing errors and freeing up human resources for more strategic endeavors. However, there are significant challenges, i.e. training and operating LLMs require substantial computational resources, making them resource-intensive. Besides, Bias in training data could lead to biased outputs, and the lack of true comprehension limits their ability to address nuanced contexts effectively. Furthermore, LLMs carry the risk of generating misinformation, emphasizing the need for cautious and responsible use.
5. The Future of LLMs
The evolution of LLMs points to several promising directions. Firstly, the integration of artificial intelligence into daily life is expected to expand, with LLMs playing critical roles in education, healthcare, and business operations. Next, efforts to enhance transparency and ethical standards will aim to reduce bias and ensure responsible model behavior. Moreover, optimizing resources for LLM training and operation is a critical area of focus, allowing smaller organizations to leverage these powerful tools. Additionally, advancements in contextual understanding will enable LLMs to handle increasingly complex scenarios with greater precision.
6. Conclusion
LLMs have been transforming how human can interact with technology, unlocking opportunities across various fields from business to education. However, their development also raises significant challenges in ethics, governance, and effective utilization. Harnessing their potential while managing the risks is key to shaping a sustainable technological future.
News: FITVAA – HTS

Vietnam Aviation Academy compiled national standards on ground radio navigation aid systems


What is a UAV? What is a drone? What is the difference between UAV and drone?
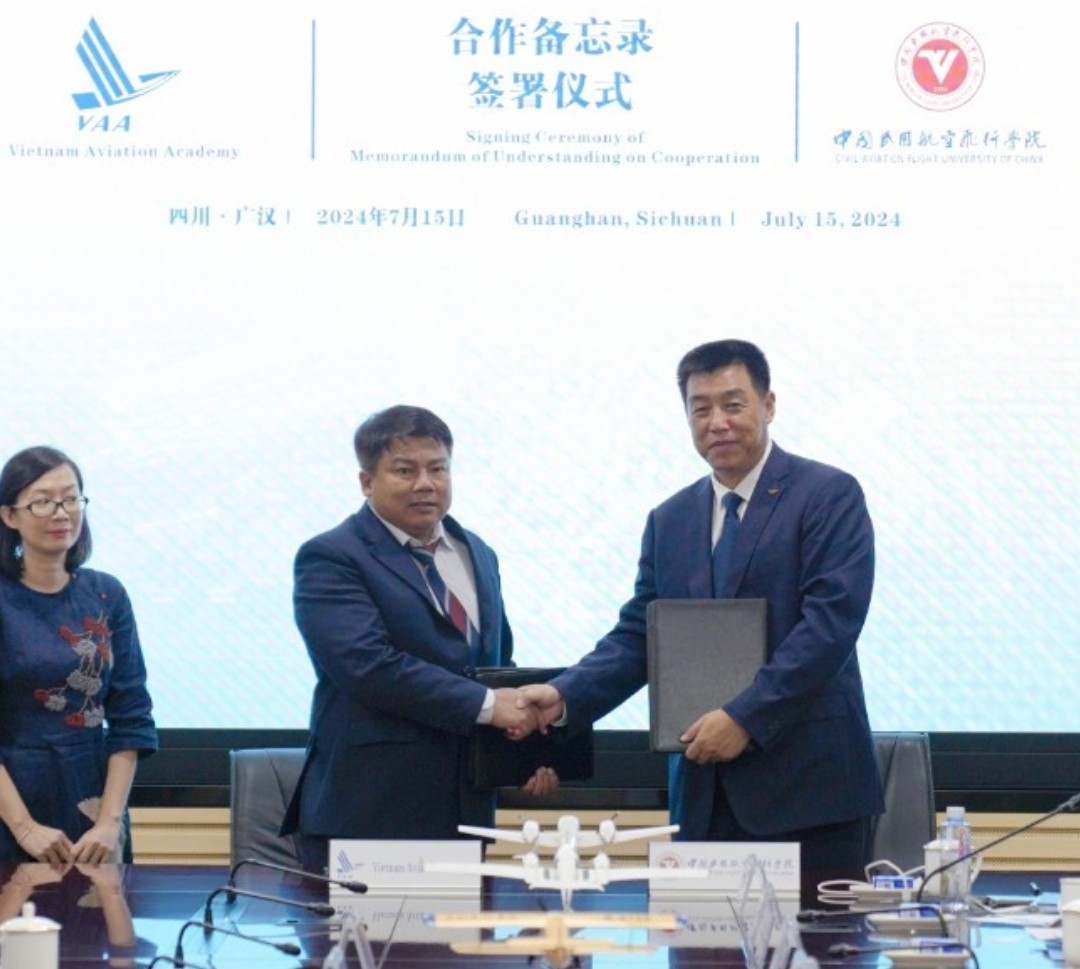


VIETNAM AVIATION ACADEMY HAS SIGNED A COOPERATION AGREEMENT WITH CIVIL AVIATION FLIGHT UNIVERSITY OF CHINA


Workshop on Developing a Strategic Plan for the Vietnam Aviation Academy: Resolutely Realizing Key Strategic Objectives

The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on the Global Economy: An Ongoing Revolution






